|
 |
|||
|
||||
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
 | |
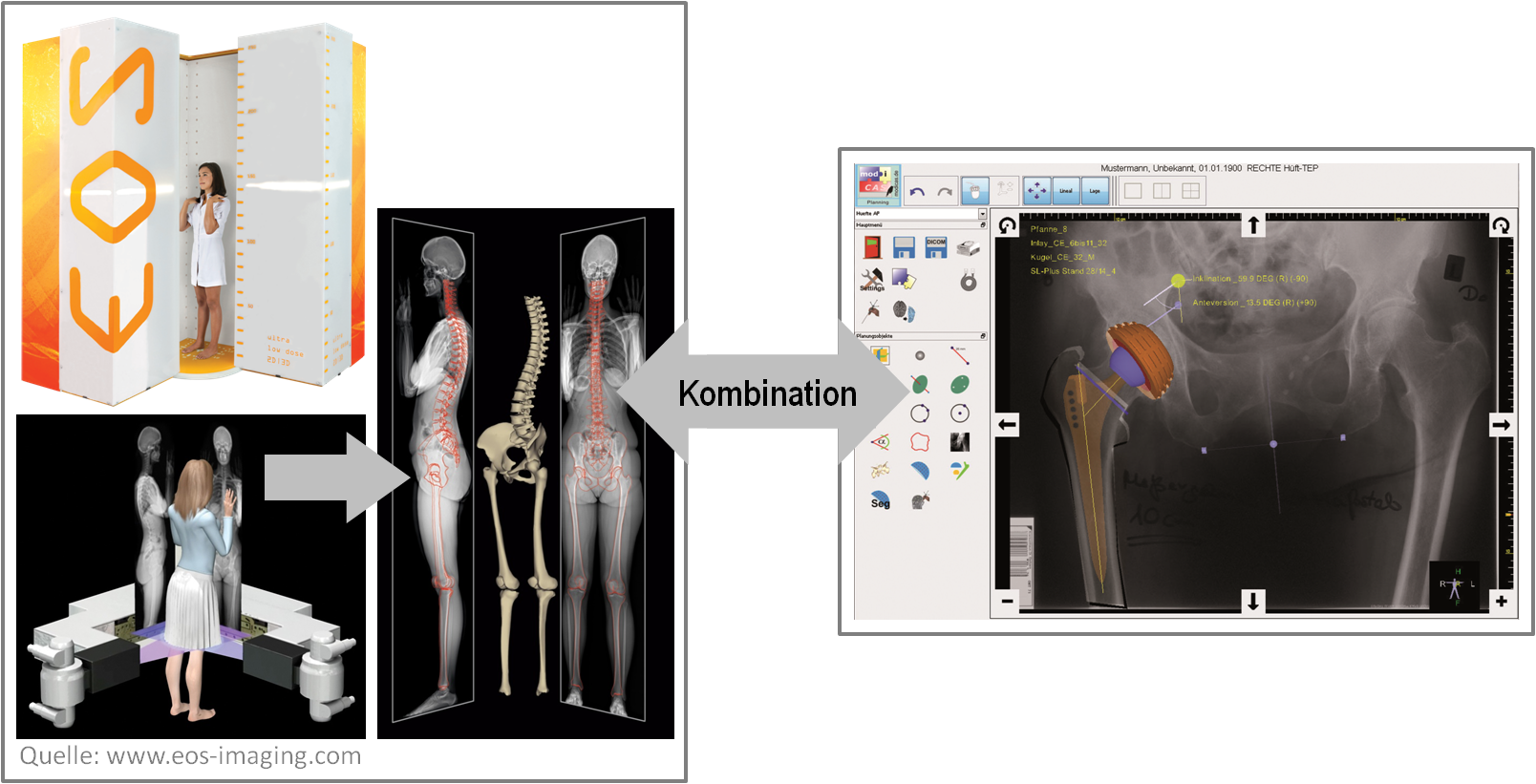
IMPLANNER - Innovative 3D planning and simulation for Hip and Knee arthroplasty
|
Projektpartner: |
|
 |
 |
| 4plus GmbH, Erlangen, Deutschland | EOS Imaging, Paris, Frankreich |
|
Deutsch |
|
|
2009 waren mehr als 81,4 Mio. Menschen in Europa, USA und Japan von Gelenkarthrose betroffen, die sehr häufig durch den Ersatz des betroffenen Gelenkes mit einer Endoprothese therapiert wird. Die Implantation der Prothese sollte sorgfältig und computergestützt geplant werden, um bereits mit diesem vorbereitenden Schritt die Grundlage für den bestmöglichen OP-Erfolg zu legen. Dazu wird im IMPLANNER-Verbundprojekt eine innovative dreidimensionale Planungssoftware entwickelt, die auf einer neuartigen, 3D Daten erzeugenden Röntgen-Bildgebung basiert. An der Universität Siegen werden semiautomatische Assistenzfunktionen vor allem für die Hüftendoprothetik konzipiert und implementiert, die dem Operateur über eine intuitive grafische Benutzeroberfläche die gleichzeitig schnelle und doch individuell angepasste, genaue Planung eines Eingriffs ermöglichen. |
|
|
|
English |
|
|
|
Osteoarthritis affected more than 81.4 million people in the five major European markets, the USA and Japan in 2009. The corresponding therapy very frequently consists in total joint replacement by using an endoprosthesis. Thorough and computer-assisted planning of the implantation is very important to prepare the optimal results of the intervention already during this first step. An innovative three-dimensional planning software which is based on a novel x-ray imaging device generating 3D data sets will be developed during the IMPLANNER joint research project to achieve this objective. At Siegen university primarily semi-automatic assistance functions for total hip replacement procedures will be investigated. An intuitive graphical user interface will support the surgeon to plan the intervention quickly, yet accurately and individually tailored to the patient. |
|
Publikationen
|
|
| gefördert im Eurostars-Programm von EUREKA und EU sowie durch das BMBF |
|
ZESS Webmaster Team 2024 Disclaimer